Dr. Judith Campisi discusses her priority research paper published in 2021 by Aging, entitled, “Cdkn1a transcript variant 2 is a marker of aging and cellular senescence.”

Behind the Study is a series of transcribed videos from researchers elaborating on their recent oncology-focused studies published by Aging. A new Behind the Study is released each Monday. Visit the Aging YouTube channel for more insights from outstanding authors.
—
Hello, my name is Judy Campisi. I am a Professor at the Buck Institute for Research on Aging and also a Senior Scientist at the Lawrence Berkeley National Lab. And my laboratory, which is a pretty international laboratory with people from Asia and Europe, published a paper in aging, “Cdkn1a transcript variant 2 is a marker of aging and cellular senescence.”
So why do we care about this?
Well, most of my lab works on a process called cellular senescence, which is a cellular response to stresses and damage, many of which increase with age. And it’s now clear from mouse models that if you eliminate senescent cells, which increase with age, you can increase the health span of a mouse – not necessarily the lifespan, but the health span. So it becomes kind of important to have ways of identifying senescent cells in detail, and we have not been able to do that so far with absolute certainty because there frankly are no senescent-specific markers. So there are markers that are commonly expressed by senescent cells, but none of them are absolutely specific.
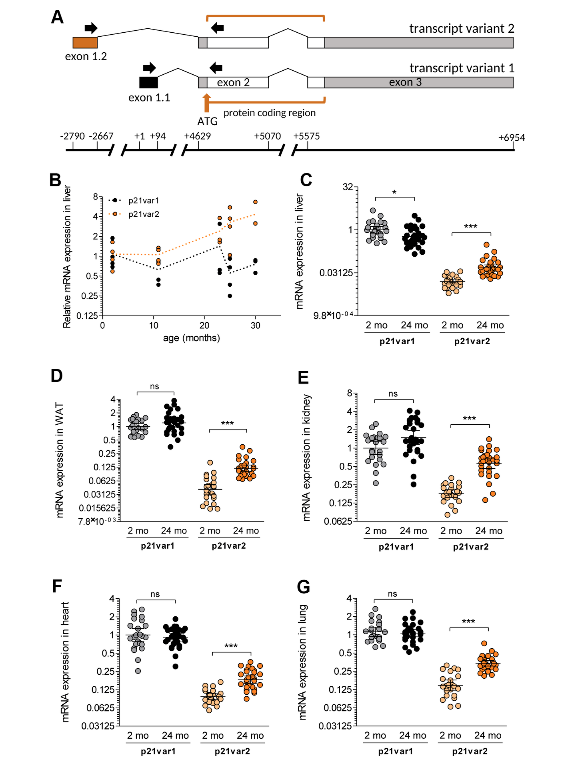
And so what we have done is we have looked at one of those markers, which is a gene called Cdkn1a and it codes for approaching, called P21. So everyone knows that P21 is one of those common biomarkers of aging, but it also is not necessarily strictly limited to aging. And what we’ve found is that there are two mRNAs that are made from that gene, that had been known before. We looked at these two mRNAs separately and found that one of them, which is called the variant 2, is a better marker of senescence and aging than the other mRNA. And that gives us a little bit of a edge in trying to unambiguously identify senescent cells in vivo and even in culture.
So the importance of this work is that it helps refine our ways of identifying these cells. We now know that these cells are important in aging, certainly in mice, probably in humans as well. So with this group of mine, many of which come from Spain or France or Russia, many of them contributed to refining this marker and allowing us to be able to have a better way of having some confidence that a senescent cell is indeed senescence.
And I can stop here.
Click here to read the full study published by Aging.
WATCH: MORE AGING VIDEOS ON LABTUBE
—
Aging is an open-access journal that publishes research papers monthly in all fields of aging research and other topics. These papers are available to read at no cost to readers on Aging-us.com. Open-access journals offer information that has the potential to benefit our societies from the inside out and may be shared with friends, neighbors, colleagues, and other researchers, far and wide.
For media inquiries, please contact [email protected].